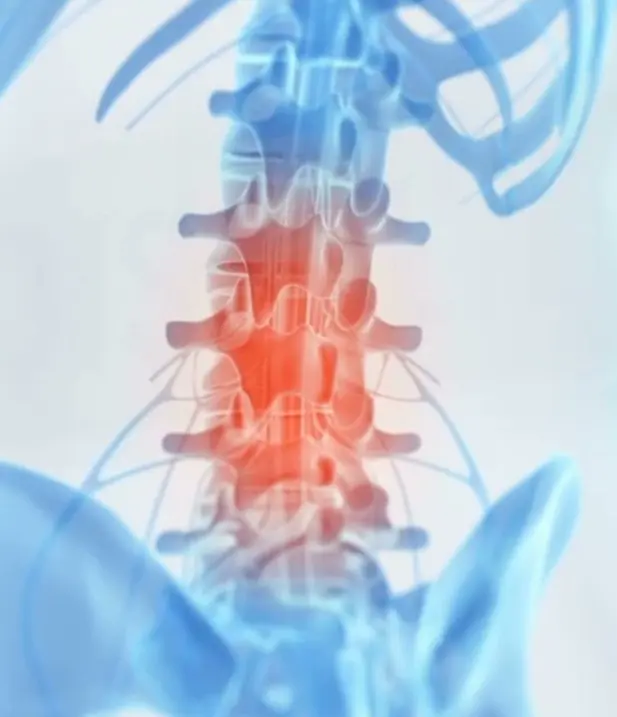
Lumbar radiculopathy is a pinched nerve in the spine that leads to a wide assortment of symptoms, including pain, numbness and tingling. It is a common contributor to back pain, and it often results from a problem with one or more of the discs in the spine. Understanding the symptoms of lumbar radiculopathy and seeking treatment from a spine health specialist could help you to reduce pain and return to your everyday activities.
Causes of Lumbar Radiculopathy
Root nerve pain in the lumbar region often develops from compression of a nerve. When the nerve is compressed at its root, it triggers symptoms such as pain that radiates into one leg, pain that gets worse by sitting or staying in one position and pain that gets worse at night. A pinched or compressed nerve also gets worse with sudden movements that put more pressure on the affected nerve. Some causes of the root nerve compression include:
- Herniated disc in the lumbar spine
- Bulging disc in the lumbar spine
- Degenerative disc disease
- Facet joint degeneration
- Cancer or infection of the vertebrae
- Osteoarthritis
- Major trauma, such as a car accident or a slip-and-fall accident on ice
- Other chronic conditions, such as diabetes or inflammation of the meningeal surfaces
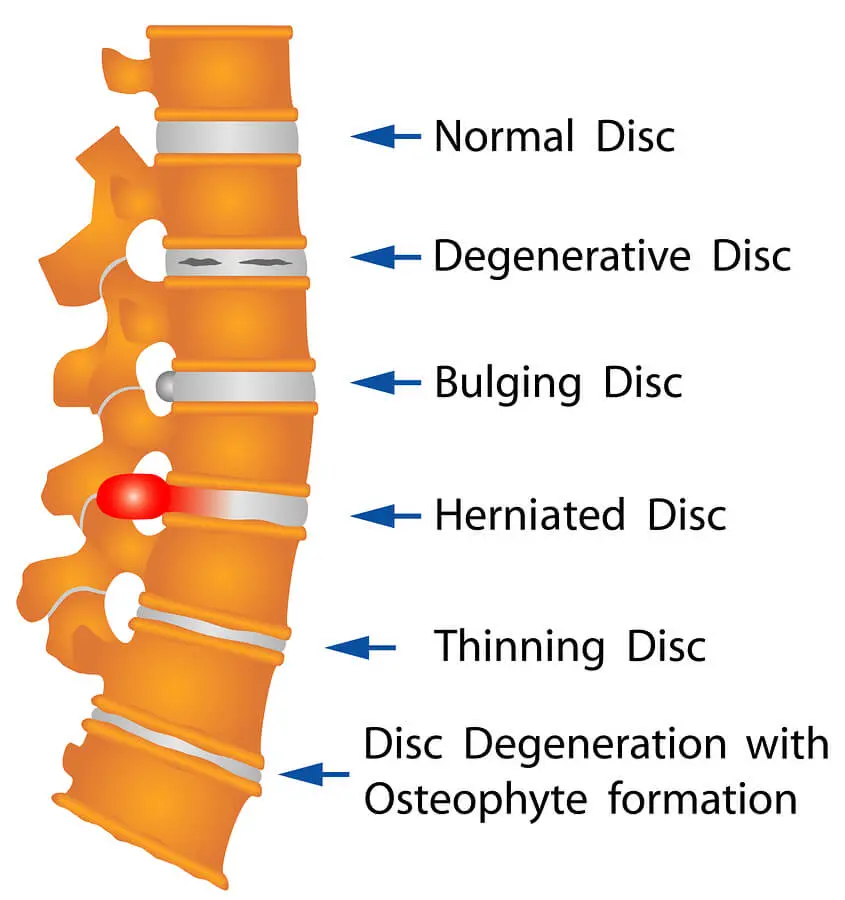
Treatments for a Herniated Disc
Back pain treatments aim to reduce the discomfort that you feel in your lower back and into your leg. For a herniated disc, there are many different treatment approaches that you and your spine health specialist might consider. In most cases, the herniation can be corrected conservatively. The available treatment options include:
- Stretching exercises as directed by the spine health specialist
- Intensive physical therapy to restore range of motion and strength
- Resistance exercises to restore spine strength
- Surgical repair of the lamina or protrusion of the disc
Treatments for a Bulging Disc
Most bulging disc treatments are conservative and focus on restoring flexibility and range of motion through physical therapy. Surgery might be indicated if therapeutic exercises do not resolve your lower back and leg pain. Treatments for bulged discs include:
- Physical therapy, heat and massage
- Core strength training exercises
- Increase in moderate activity such as walking
- Posture correction
- Implementation of an anti-inflammatory diet
It is a condition wherein the inter-vertebral disc on the spine herniates which causes pressure and impingement on nerves and their structures causing pain. The term radiculopathy comes from the word Radix, which means root. This condition gives the patient weakness, numbness and pain in the back and the feet. The term herniation generally refers to slipping or sliding. The term sciatica generally refers to pain or numbness of the leg due to the compression of the sciatic nerve.
The sciatic nerve can be found at the back of each leg but it originates in the lower spine. When nerves are compressed due to herniation and pressure, the blood flow to those vital parts is impeded, thus making the nerve weak and unable to perform its function properly.
The pain that patients with lumbar radiculopathy experience varies from case to case. Since it is very subjective, it is very difficult to compare accurately. Usually, the pain in this condition is only manifested at one leg. The affected leg may feel very weak, numb and tingling. It is important for patients and their families to know specific characteristics of it.
The pain in such cases starts gradually. It is not sudden but it may increase in intensity over time. It usually begins mostly at night, after sitting or standing for too long. The pain may also be felt when the patient coughs, sneezes or sometimes even laughs. In some cases, it can be severe leading to temporary disability.
Pain can definitely affect a person’s performance. He may not be able to move correctly, he is not able to participate in a lot of daily routines and most importantly, the patient easily loses his or her focus. This can affect the patient’s job and lifestyle. As soon as lumbar radiculopathy is detected through an imaging study like MRI, the patient should undergo some serious physical therapy. It will subside if the underlying condition is solved.
Contact Us
Error: Contact form not found.

Midtown
7 W 45th St floor 9
New York, NY 10036
Downtown
65 Broadway Suite 603
New York, NY 10006